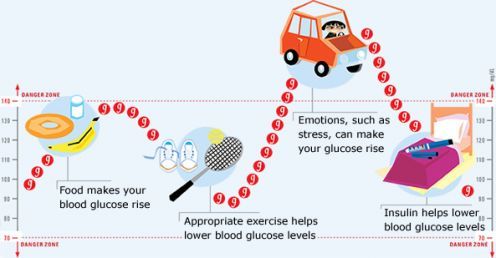
Normal blood glucose levels should remain within a range that is neither too high nor too low
Too low a normal blood glucose level can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis and even hypoglycemia. Too high a normal blood glucose level can cause hypoglycemia and coma. It can also cause permanent nerve damage to organs. When blood glucose levels fall too far, there are usually warning symptoms.
Too much insulin may occur when high blood glucose levels are present. Insulin is the key hormone in the body that controls the amount of glucose that is being consumed and used by cells. A normal blood glucose level can be measured by a blood glucose test. A blood glucose test is performed to check the levels of blood glucose in the blood.
The normal blood glucose levels can fluctuate, depending on how the body responds. Blood glucose levels in people with diabetes tend to be lower than normal levels. When there are too many carbohydrates eaten, the blood glucose tends to decrease. When glucose levels drop too low, the brain can not process glucose effectively and insulin production increases causing hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia occurs when sugar is not absorbed into the body properly. This can cause fainting, weakness, dizziness, disorientation, and loss of consciousness. The most serious and immediate hypoglycemic reaction is loss of consciousness. Other symptoms of hypoglycemia include seizures, coma, and cardiac arrest. If hypoglycemia occurs, seek immediate medical attention.
If abnormal blood glucose levels are present, the kidneys can flush out some of the excess glucose produced in the blood. Glucose that is not eliminated from the body is usually converted to glycogen in the liver, where it is converted back to glucose and used as fuel.
The glycogen is then stored as fat. A person with diabetes may not have enough glycogen. If there is enough glycogen in the bloodstream, the liver will break down glycogen stores as fat. This is when weight gain occurs. The excess energy is then burned off in the metabolic process.

Diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, occurs when the level of ketones in the blood exceeds normal levels. It could be caused by too high blood sugar. Ketones can cause cell burnout to form ketone bodies. They can then enter the bloodstream, where they can be deposited in the bladder, lungs, liver, kidneys, pancreas, or brain.
Kidney stones can also form from ketone bodies. They form when the kidneys are unable to use glucose efficiently. People with kidney problems may suffer from low urine levels, which causes them to excrete more urine than they take in, resulting in them urine becomes cloudy. This is often referred to as ketoacidosis.
In advanced stages of diabetic kidney failure, protein is no longer able to bind with the proteins in the blood, preventing further sugar from being absorbed into the body. This prevents insulin from binding properly with the glucose, resulting in diabetes. The kidneys can eventually fail, and a person who suffers from diabetes will eventually experience organ failure.
Normal blood glucose levels are maintained by the use of insulin. Insulin is secreted by the pancreas. The pancreas creates insulin by breaking down stored sugar in the blood into glucose. There are certain foods that trigger insulin production, such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
High blood glucose levels can be managed by diet and exercise. However, the effects of excessive levels of sugar on the body are only temporary. If these levels continue to be present, treatment will need to be made. The most common side effects of high levels of sugar are vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
High blood glucose levels are treatable by using a variety of methods, depending on the individual's case. Blood sugar levels that are too high or too low can be corrected with drugs and therapy. If you are dealing with diabetes, talk to your doctor and your health care provider.